
Its strong negative charge is an important factor in evading phagocytosis. The outer membrane has several specialized functions. Consists of lipopolysaccharide (LPS), lipoproteins, phospholipids. Has an outer membrane outside the peptidoglycan layer. One or very few layers of peptidoglycan.  What part would be attacked by antibiotics and why? What would this do to the cell. Analyze the cell wall of a Gram + bacteria. Gram + Cell Wall What do the green spheres represent? What do the blue spheres represent? Stains Purple during Gram Stain Lab test. Thick layer (rigid structure) of peptidoglycan. The result is a 3-D meshwork held together by covalent bonds Tetrapeptide chain Peptidoglycan Peptide bridge Tetrapeptide chain.
What part would be attacked by antibiotics and why? What would this do to the cell. Analyze the cell wall of a Gram + bacteria. Gram + Cell Wall What do the green spheres represent? What do the blue spheres represent? Stains Purple during Gram Stain Lab test. Thick layer (rigid structure) of peptidoglycan. The result is a 3-D meshwork held together by covalent bonds Tetrapeptide chain Peptidoglycan Peptide bridge Tetrapeptide chain. 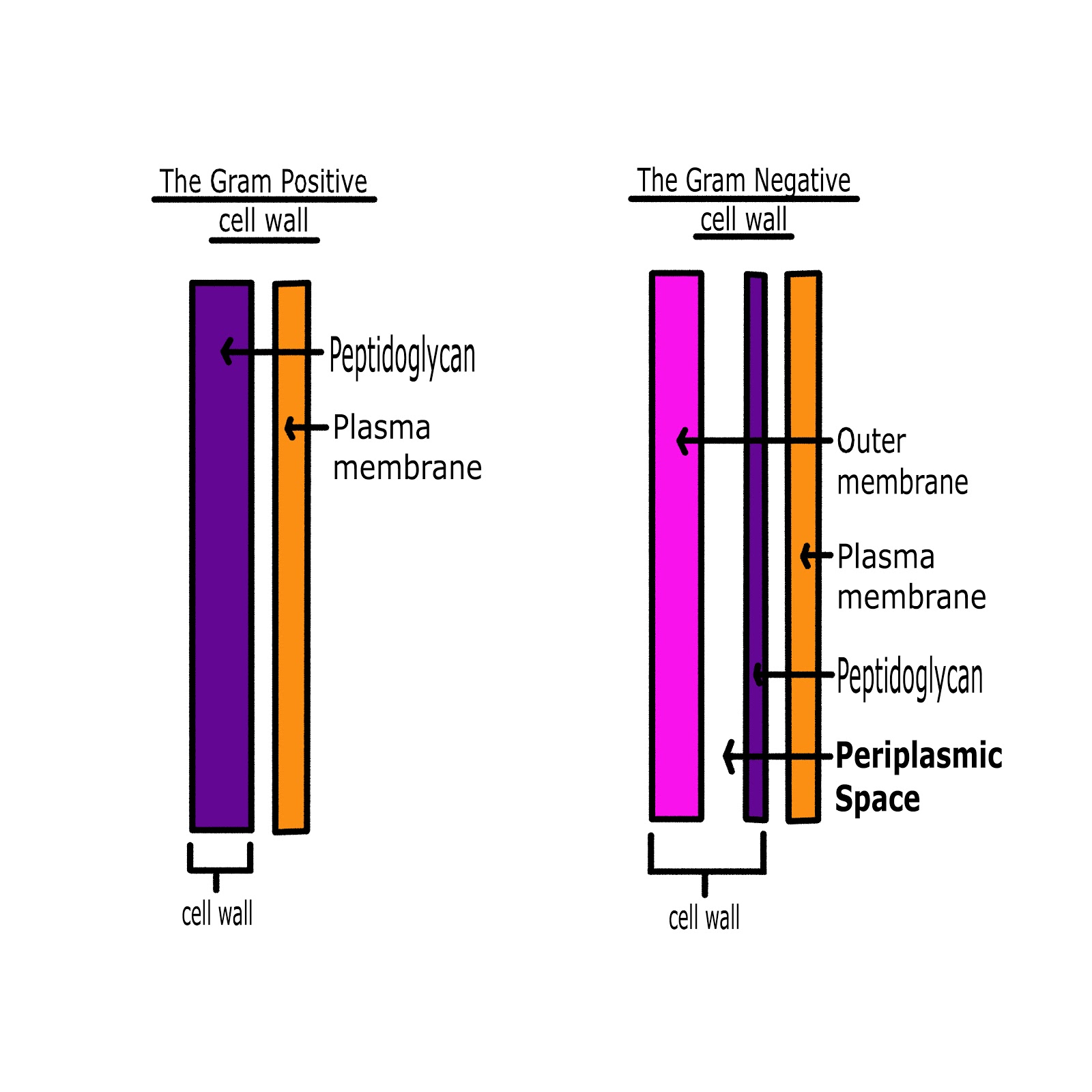
Tetrapeptide chains are linked by peptide cross-bridges.Covalently attached to each NAM is a tetrapeptide chain.Adjacent rows are linked by polypeptides.Monosaccharides called N-acetylglucosamine (NAG) and N-acetylmuramicacid (NAM).Alternating rows of 10-65 sugars to form a carbohydrate “backbone”.Peptidoglycanconsists of repeating disaccharideattached by polypeptides to form a lattice that surrounds and protects the entire cell.
 Composed of macromolecular network called peptidoglycan. Major function is to prevent bacterial cells from rupturing. Protects it and the interior of the cell from adverse changes in the outside environment. Surrounds the underlying, fragile plasma (cytoplasmic) membrane. Is a complex, semi-rigid structure responsible for the shapeof the cell as well as the size. The bacterial Cell Wall Gram + & Gram – Bacteria
Composed of macromolecular network called peptidoglycan. Major function is to prevent bacterial cells from rupturing. Protects it and the interior of the cell from adverse changes in the outside environment. Surrounds the underlying, fragile plasma (cytoplasmic) membrane. Is a complex, semi-rigid structure responsible for the shapeof the cell as well as the size. The bacterial Cell Wall Gram + & Gram – Bacteria







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
